"Whether it's kinetic or potential, both of them are energy!" 2/4
Image:
Summary:
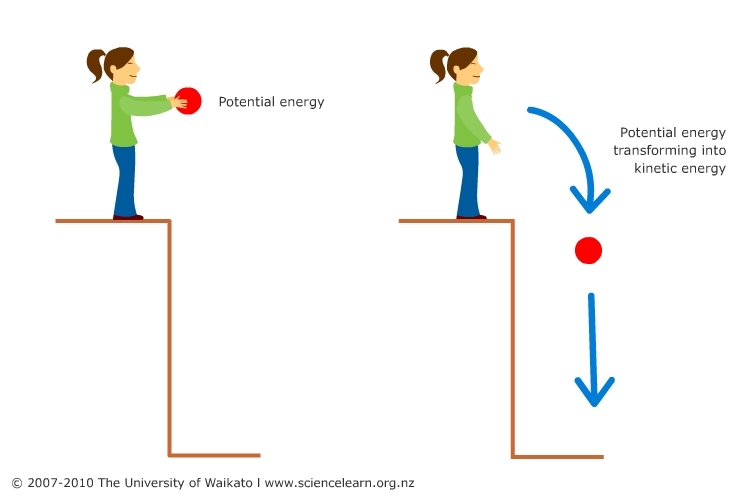
Everyone assumes they know what energy is, but I bet they don't know the whole story? Actually, there are two main branches of energy consisting of kinetic and potential energy. Kinetic energy is energy an object has because it is in motion whereas potential energy is energy that is waiting to be used hence the name potential. Potential energy itself branches down into three groups including gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and chemical potential energy. Gravatational potenttial energy is potential energy due to an objects position. An example of this would be a boulder sitting high atop a mountain. Elastic potential energy is potential energy due to the compression or expansion of someone or something. For instance, stretching a rubber band without releasing it would be elastic potential energy. Chemical potential energy is potential energy that is held within the chemical bonds of an object or substance. A form of chemical potential energy would be the energy stored in gasoline before it is used.
S&EP-Using Math:
Just like a majority of physics, both potential and kinetic energy have formulas that proved to be useful this week. The formula for kinetic energy is .5(mass x speed^2) or (mass x speed)(mass x speed)/2. As for potential energy, the formula is (mass x gravity x height). Along with this I used logical math to determine solution to problems such as which diver had to put in more work to reach their board. I used logical math to say the diver who was on the higher board, diver a, and it made sense because the higher you are the more you have to travel from the ground. Another logical math problem was if the potential energy of a ball at 2 meters high is 1.96 if it falls, what would be its kinetic energy right before it hits the ground. This was a bit fuzzy at first but eventually I began to understand that as an object begins moving the potential energy is decresing the same amount as the kinetic energy is increasing meaning the answer is 1.96.
XCC-Cause and Effect:
Throughout Newton's three laws that constantly pop up in ours lives, there is a clear cause and effect relationship. Newton's third law, "Every action has an equal and opposite reaction," is a good example of a cause an effect relationship. The cause would be "the action" and the effect would be "the equal and opposite reaction." Looking at this through the example of a bouncy ball, we can see that the cause would be throwing the ball towards the ground and the effect would be the ball bouncing back in the opposite direction. Newton's first law, "An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force," is also a example of a cause and effect relationship. In this law, the unbalanced force is the cause and it causes the object in motion to stop or vice versa. An example of this, would be a globe. A globe stays in position until someone spins it, and that someone who spins it is a the cause and the effect is that the globe 'begins to spin.
Multiplier: This week I was a mutant, to be more specific a wanderer because I tried to share the new information about energy with my tablemates.
 |
| sciencelearn.org.nz |
Summary:
Everyone assumes they know what energy is, but I bet they don't know the whole story? Actually, there are two main branches of energy consisting of kinetic and potential energy. Kinetic energy is energy an object has because it is in motion whereas potential energy is energy that is waiting to be used hence the name potential. Potential energy itself branches down into three groups including gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and chemical potential energy. Gravatational potenttial energy is potential energy due to an objects position. An example of this would be a boulder sitting high atop a mountain. Elastic potential energy is potential energy due to the compression or expansion of someone or something. For instance, stretching a rubber band without releasing it would be elastic potential energy. Chemical potential energy is potential energy that is held within the chemical bonds of an object or substance. A form of chemical potential energy would be the energy stored in gasoline before it is used.
S&EP-Using Math:
Just like a majority of physics, both potential and kinetic energy have formulas that proved to be useful this week. The formula for kinetic energy is .5(mass x speed^2) or (mass x speed)(mass x speed)/2. As for potential energy, the formula is (mass x gravity x height). Along with this I used logical math to determine solution to problems such as which diver had to put in more work to reach their board. I used logical math to say the diver who was on the higher board, diver a, and it made sense because the higher you are the more you have to travel from the ground. Another logical math problem was if the potential energy of a ball at 2 meters high is 1.96 if it falls, what would be its kinetic energy right before it hits the ground. This was a bit fuzzy at first but eventually I began to understand that as an object begins moving the potential energy is decresing the same amount as the kinetic energy is increasing meaning the answer is 1.96.
XCC-Cause and Effect:
Throughout Newton's three laws that constantly pop up in ours lives, there is a clear cause and effect relationship. Newton's third law, "Every action has an equal and opposite reaction," is a good example of a cause an effect relationship. The cause would be "the action" and the effect would be "the equal and opposite reaction." Looking at this through the example of a bouncy ball, we can see that the cause would be throwing the ball towards the ground and the effect would be the ball bouncing back in the opposite direction. Newton's first law, "An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force," is also a example of a cause and effect relationship. In this law, the unbalanced force is the cause and it causes the object in motion to stop or vice versa. An example of this, would be a globe. A globe stays in position until someone spins it, and that someone who spins it is a the cause and the effect is that the globe 'begins to spin.
Multiplier: This week I was a mutant, to be more specific a wanderer because I tried to share the new information about energy with my tablemates.


Comments
Post a Comment